MERGE IN PANDAS
In this tutorial, we are going to learn about the merge function in pandas and how we can join or merge two dataframes with the commonalities of data using inner, outer, left and right join.
What is Merge in Pandas?
We have been working with 2-D data which is rows and columns in Pandas. In order to go on a higher understanding of what we can do with dataframes that are mostly identical and somehow would join them in order to merge the common values. We use a function called merge() in pandas that takes the commonalities of two dataframes just like we do in SQL. The Syntax for merge in pandas is:
DataFrame.merge(self, right, how=’inner’, on=None, left_on=None, right_on=None, left_index=False, right_index=False, sort=False, suffixes=(‘_x’, ‘_y’), copy=True, indicator=False, validate=None)
Inner Join
Let’s merge two dataframes which will have common indexes and see different ways to merge their values:
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Country':["India", "USA", "Canada","Pakistan"],
'Population':[1352642280, 329968629, 35151728, 212742631]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Country':["India", "USA", "Brazil","Bangladesh"],
'Area/sqkm2':[3287263,9834000, 8511000, 147570]})
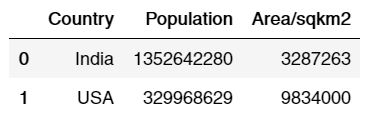
df3 = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Country')
df3
Output:
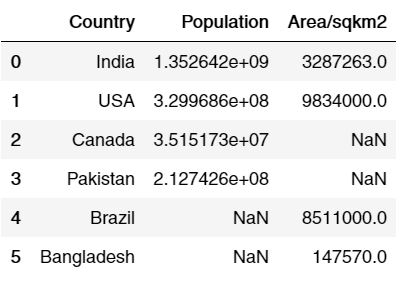
Above you can see that a simple merge has been displayed which displays the common values present in both the data frames, if you want to visually see this, then here is a quick at what exactly happened.
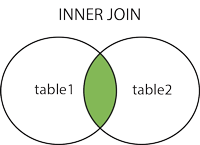
Courtesy: w3schools.com
By default, merge creates the inner join which only takes values that are common, in our case India and USA were present in both the dataframes, so the merge function only printed values that were common in both the dataframes while ignoring other countries. However, we can create, left join, right join and outer join as well by predefining the ‘how’ attribute.
Left Merge in Pandas
As the name suggests the left join will only display values that are common between two dataframes as well as present fully in the left or first dataframe in our case.
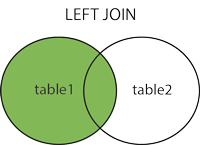
Courtesy: w3schools.com
df3 = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Country', how='left') df3
Output:

You can see that the values that aren’t present or missing during the merge process have been replaced by NaN term.
Right Merge in Pandas
The left join will only display values that are common between two dataframes as well as present fully in the right dataframe in our case.
Courtesy: w3schools.com
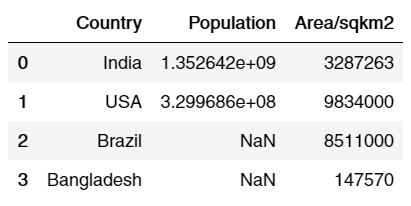
df3 = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Country', how='right') df3
Outer Join
The outer join will merge all the values together of both the dataframes
Courtesy: w3schools.com
df3 = pd.merge(df1, df2, on='Country', how='outer') df3
Output: